Crafting Your Career: Becoming a DevOps Architect
Embark on a journey into the world of DevOps architecture with this engaging title that sets the stage for an informative discussion. Dive into the role, responsibilities, and essential skills required for excelling as a DevOps architect.
Introduction to DevOps Architect
A DevOps architect plays a crucial role in bridging the gap between development and operations teams, focusing on improving collaboration, automation, and efficiency in the software development lifecycle.
Primary Responsibilities of a DevOps Architect
- Designing and implementing DevOps strategies and practices within an organization.
- Automating processes to streamline software delivery and deployment.
- Collaborating with cross-functional teams to ensure seamless integration of DevOps practices.
- Monitoring and optimizing system performance and reliability.
- Providing guidance on best practices for continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD).
Key Skills and Expertise Required
- Strong knowledge of cloud platforms and infrastructure as code tools like Terraform.
- Proficiency in scripting languages such as Python, Ruby, or Shell scripting.
- Experience with containerization technologies like Docker and Kubernetes.
- Ability to work with configuration management tools like Ansible, Puppet, or Chef.
- Excellent communication and collaboration skills to work effectively with diverse teams.
DevOps Tools and Technologies
DevOps architects rely on a variety of tools and technologies to streamline the software development process and improve collaboration between development and operations teams. These tools play a crucial role in achieving continuous integration, delivery, and deployment.
Essential Tools for DevOps Architects
- Jenkins: A popular automation server that helps in automating the software development process, including building, testing, and deploying code.
- Git: A distributed version control system that allows teams to collaborate on code and track changes efficiently.
- Ansible: An open-source automation tool that simplifies the configuration management and deployment of applications.
- Docker: A containerization platform that enables developers to package applications and their dependencies into lightweight containers.
- Kubernetes: An open-source container orchestration tool for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
Importance of Automation Tools in DevOps
Automation tools are essential in DevOps practices as they help in reducing manual errors, speeding up the development process, and ensuring consistency across environments. By automating repetitive tasks such as testing, deployment, and monitoring, teams can focus more on innovation and delivering value to customers.
Utilization of Containerization Tools like Docker and Kubernetes
Containerization tools like Docker and Kubernetes have revolutionized the way applications are deployed and managed in DevOps environments. Docker allows developers to create isolated containers for their applications, making it easier to maintain consistency between development, testing, and production environments.
Kubernetes, on the other hand, helps in automating the deployment and scaling of these containers, ensuring high availability and resilience in production environments.
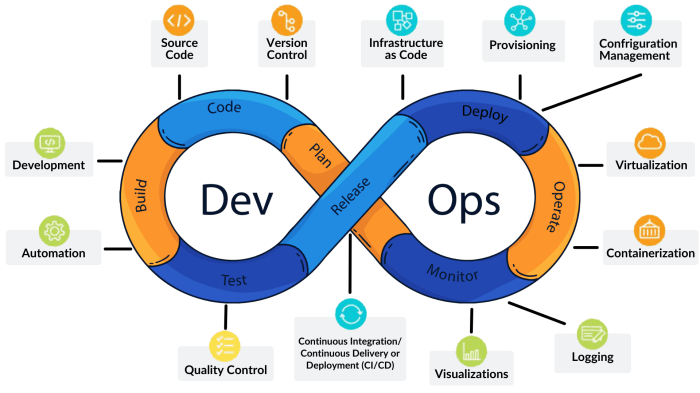
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
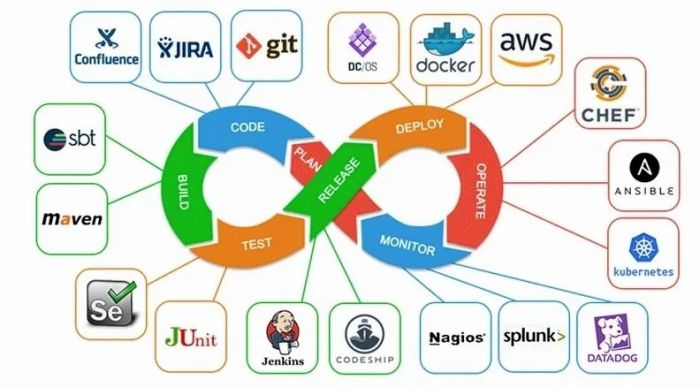
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) is a crucial component of the DevOps pipeline that focuses on automating the process of integrating code changes and deploying them to production environments. It helps in ensuring rapid and reliable delivery of software updates.
Significance of CI/CD in the DevOps pipeline
CI/CD plays a vital role in streamlining the software development process by automating the build, test, and deployment phases. It helps in reducing manual errors, improving collaboration between development and operations teams, and increasing the overall efficiency of the development lifecycle.
Popular CI/CD Tools
- Jenkins: An open-source automation server widely used for building, testing, and deploying software.
- GitLab CI/CD: Integrated into GitLab for automating the software development lifecycle.
- CircleCI: A cloud-based CI/CD tool that automates the testing and deployment process.
- Travis CI: A popular CI/CD tool for testing and deploying code changes.
Setting up a CI/CD pipeline for software development
Setting up a CI/CD pipeline involves the following steps:
- Version control: Ensure code changes are tracked using a version control system like Git.
- Automated build: Use a CI tool like Jenkins to automate the process of building the application.
- Automated testing: Integrate automated testing into the pipeline to ensure code quality.
- Deployment automation: Use tools like Ansible or Docker for automating the deployment process.
- Monitoring and feedback: Implement monitoring tools to track the performance of the application and gather feedback for continuous improvement.
Cloud Computing in DevOps
Cloud computing plays a crucial role in DevOps architecture by providing the necessary infrastructure and services for continuous integration, deployment, and delivery of software applications. Cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer a wide range of tools and resources that DevOps architects leverage to enhance scalability, flexibility, and efficiency in their workflows.
Cloud Service Models
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):In the IaaS model, cloud providers offer virtualized resources like virtual machines, storage, and networking. DevOps architects can use IaaS to quickly provision and manage infrastructure components, allowing for easier scalability and automation of deployments.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS):PaaS provides a platform for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. DevOps architects can take advantage of PaaS offerings to streamline application development and deployment processes.
- Software as a Service (SaaS):SaaS delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for users to install and maintain the software locally. DevOps architects can utilize SaaS solutions to integrate third-party tools and services seamlessly into their workflows.
Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud services enable DevOps architects to scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency. By utilizing cloud platforms, DevOps teams can automate infrastructure provisioning, deployment, and monitoring, resulting in faster time-to-market and improved reliability of applications.
Additionally, cloud services provide the flexibility to experiment with new technologies and adopt innovative practices without significant upfront investments.
Closure
In conclusion, the role of a DevOps architect is crucial in the realm of software development, utilizing cutting-edge tools and technologies to streamline processes and ensure efficiency. Embrace the challenges and rewards that come with this dynamic position in the tech industry.
Essential FAQs
What is the primary responsibility of a DevOps architect?
The primary responsibility of a DevOps architect is to design, implement, and maintain the infrastructure and tools needed for software development and deployment.
How are containerization tools like Docker and Kubernetes used in DevOps practices?
Containerization tools like Docker and Kubernetes are used in DevOps practices to create portable and scalable environments for deploying applications consistently across different systems.
Why is CI/CD significant in the DevOps pipeline?
CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) is crucial in the DevOps pipeline as it allows for automated testing, integration, and deployment of code changes, ensuring a rapid and reliable software release process.
How do DevOps architects leverage cloud services for scalability and flexibility?
DevOps architects leverage cloud services like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud to scale infrastructure resources dynamically based on demand, enabling flexibility, cost-efficiency, and improved performance.




